Cyclohexanone, a symmetrical cyclic ketone, is an important intermediate in the production of nylon. Isophorone, derived from acetone, is an unsaturated, asymmetrical ketone that is the precursor to other polymers. Muscone, 3-methylpentadecanone, is an pheromone. Another cyclic ketone is cyclobutanone, having the formula C 4 H 6 O.

In general, the moisture content in nylon is a key variable affecting processing (polymerization, compounding, molding, welding, etc.) and end-use performances (mechanical, dimensional, surface appearance, etc.). The absorbed water in polymer behaves like plasticizer, which affects material properties such as strength, stiffness, and ductility.

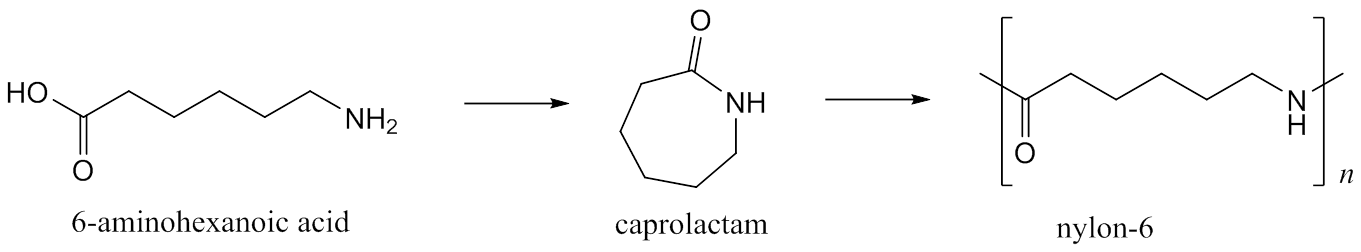
The two most common nylon fibers are nylon 6 (i.e Poly-caprolactam, a cyclic nylon intermediate) and nylon 66 (poly-hexamethylene adiamide). Nylon fibers fall in the category of condensation copolymers that are manufactured by the reaction of equal parts of diamine and dicarboxylic acid.
The two most common versions are nylon 66 (polyhexamethylene adiamide) and nylon 6 (Polycaprolactam, a cyclic nylon intermediate). Nylon 66 has been preferred in North American markets, whereas nylon 6 is much more popular in Europe and elsewhere.
Nylon washes easily. the most widely used nylon products in the textile industry are formed of nylon 6 and nylon 6/6. Nylon is used both alone and in blends with other fibers.000 to 20. and coatings of metal objects. toughness at low temperatures.
The two most common versions are nylon 6/6 (polyhexamethylene adiamide) and nylon 6 (polycaprolactam, a cyclic nylon intermediate). Raw materials for these are variable and sources used commercially are benzene (from coke production or oil refining), furfural (from oat hulls or corn cobs) or 1,4-butadiene (from oil refining).



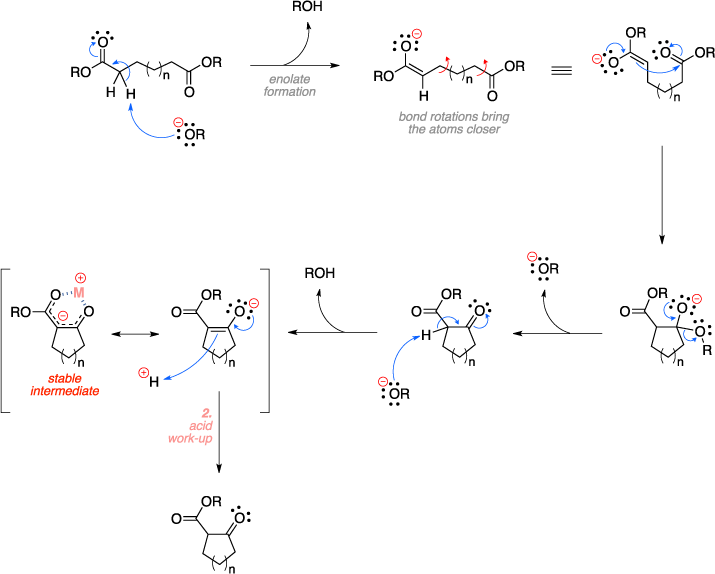
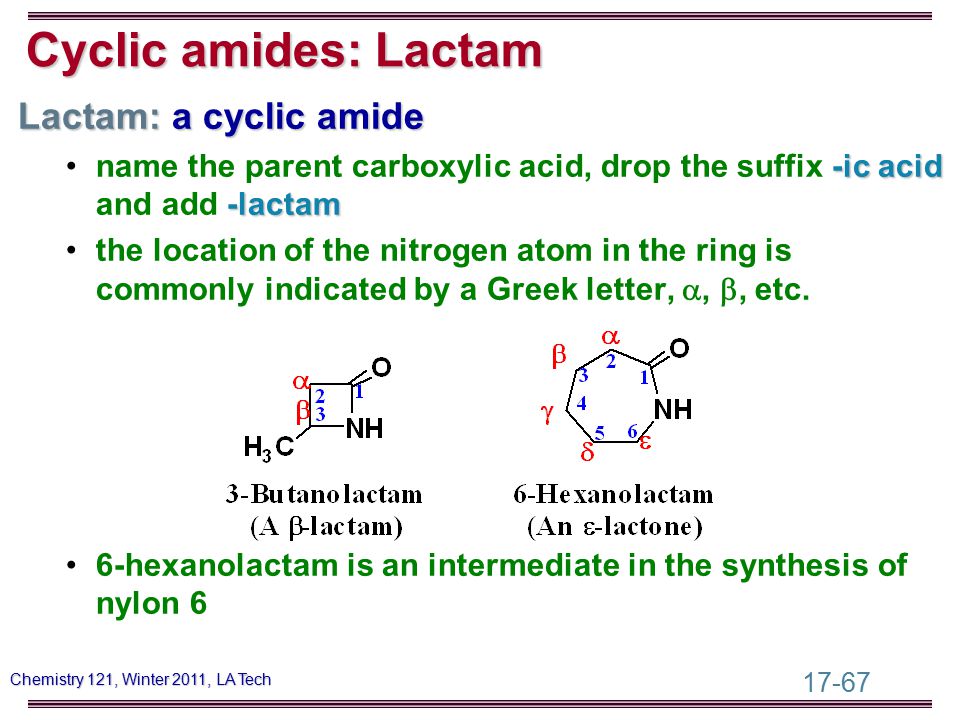
How can the answer be improved?
The two most common nylon fibers are nylon 6 (Polycaprolactam, a cyclic nylon intermediate) and nylon 66 (polyhexamethylene adiamide). Nylon fibers consists the chemical elements such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen.
Nylon was developed in the 1930s by scientists at Du Pont, headed by an American chemist Wallace Hume Caruthers (1896–1937). It is a polyamide fibre, derived from a diamine and a dicarboxylic acid. The two most common versions are nylon 66 (polyhexamethylene adiamide) and nylon 6 (Polycaprolactam, a cyclic nylon intermediate).

In the case of Nylon 6 and Nylon 6/6.47° tetrahedral bonds of singly-bonded carbon atoms. and lower melting point than Nylon 6/6. If subjected to cold drawing afterwards. even though the properties may not be as good as Nylon 6/6 in dry conditions. and the material acquires additional tensile strength.