
Lidocaine, instilled intranasally, was superior to placebo in a randomized, double-blind study for the treatment of migraine headache. Lidocaine provided significant relief of headache pain, nausea, and photophobia within 5 minutes compared to placebo.
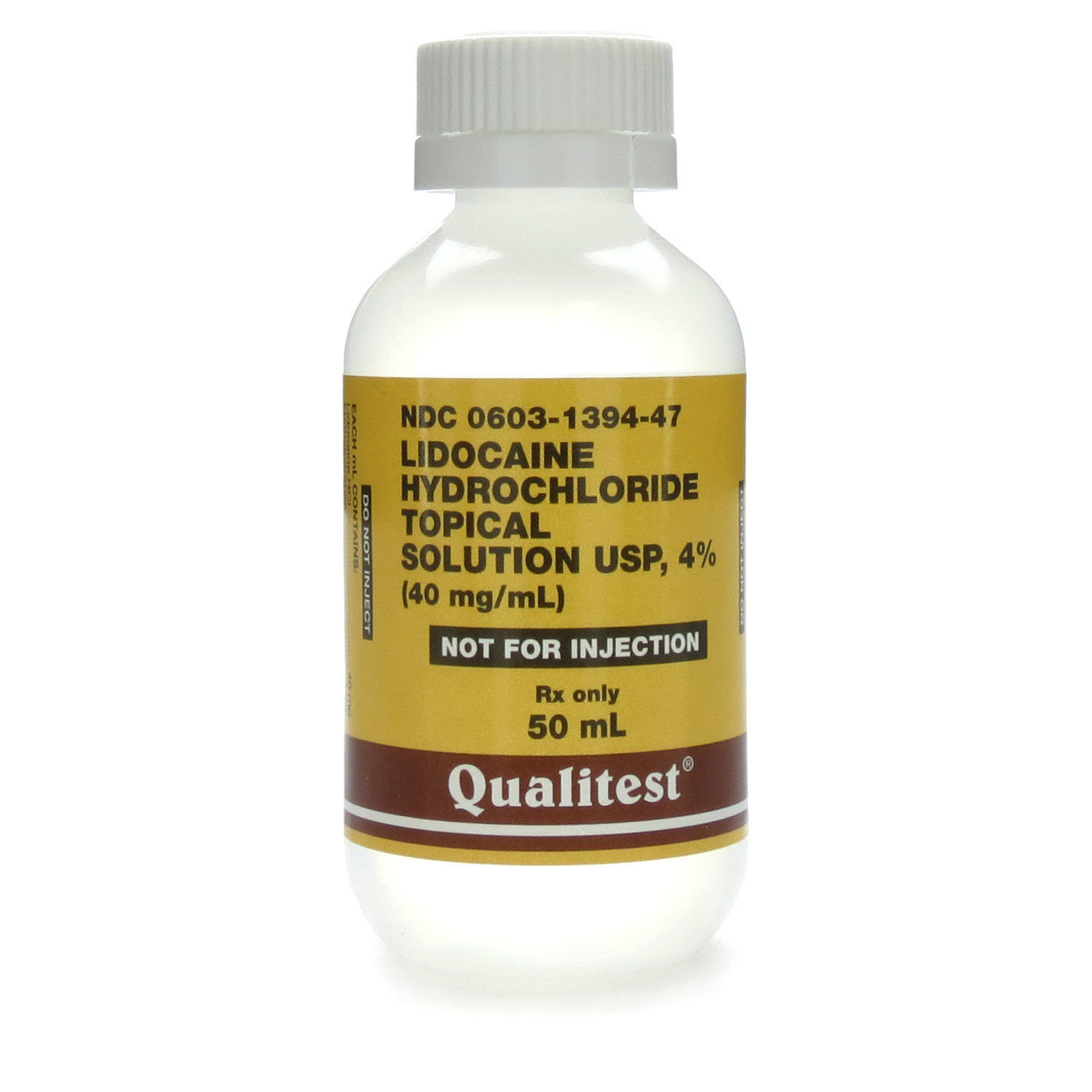
Lidocaine topical comes in many different forms for different uses. Lidocaine topical cream, lotion, spray, solution, film, and transdermal patch are generally for use on the skin only. Lidocaine topical gel, mucus membrane solution, and oral spray are for use in the mouth or on the gums.
Lidocaine viscous comes as a thick liquid and should be shaken well before using. Lidocaine viscous usually is used as needed but not more frequently than every 3 hours, with a maximum of 8 doses in 24 hours. In ren under 3 years of age, do not use more frequently than every 3 hours, with a maximum of 4 doses in 12 hours.

How can the answer be improved?
Lidocaine, also known as xylocaine and lignocaine, is a medication used to numb tissue in a specific area (local anesthetic). It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia and to perform nerve blocks .

Jul 05, 2018 · Lidocaine Topical Oral Solution – Clinical Pharmacology Mechanism of Action Lidocaine stabilizes the neuronal membrane by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required for the initiation and conduction of impulses, thereby effecting local anesthetic action.


Find patient medical information for Lidocaine Viscous Mucous Membrane on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings and user ratings.
Lidocaine viscous solution is a local anesthetic that is applied topically to treat painful mucous membranes or throat pain associated with oral diseases and for procedures involving the mouth or throat.

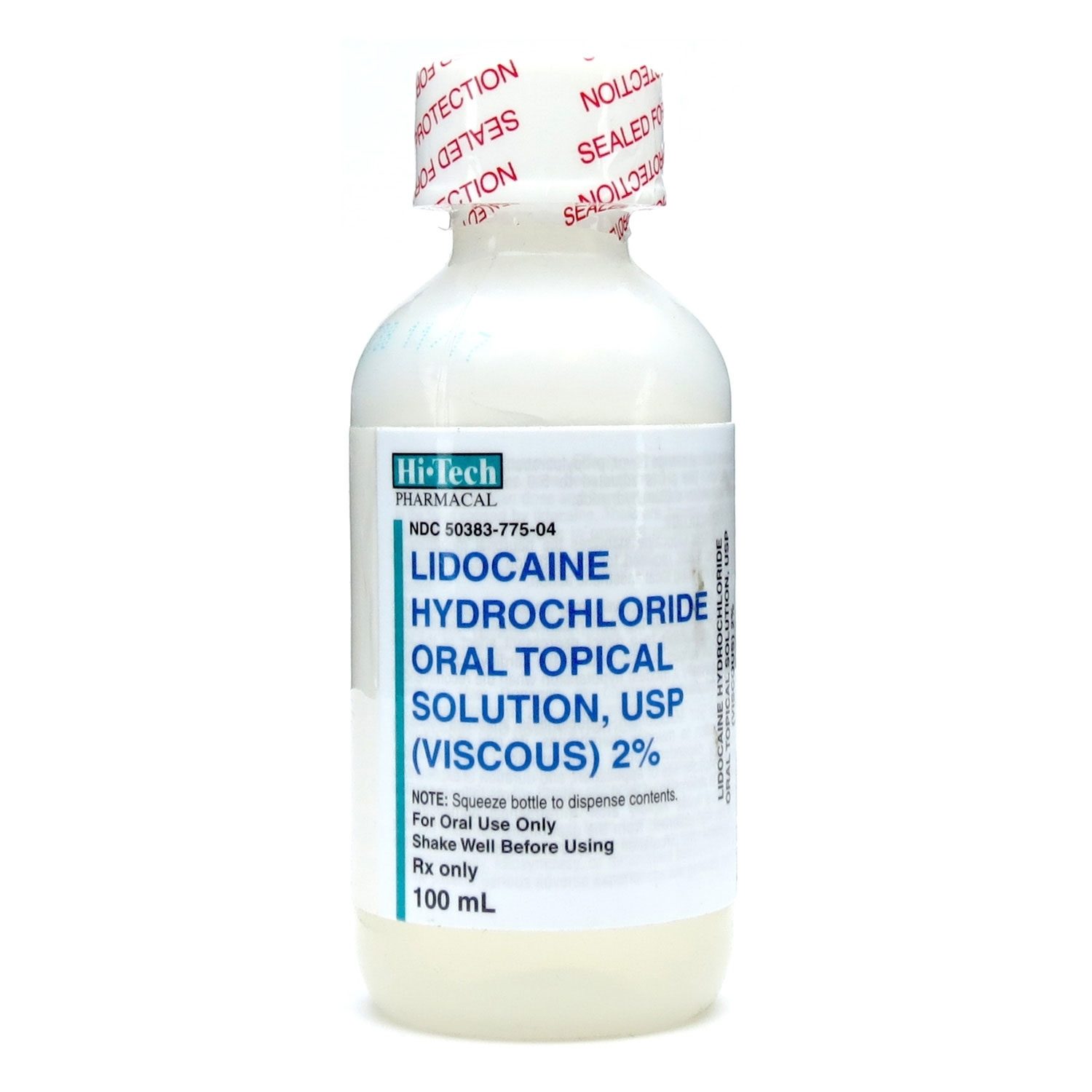


Oral viscous lidocaine solution is not approved to treat teething pain, and use in infants and ren can cause serious harm, including death.
Aprepitant, when administered as a 3-day oral regimen (125 mg/80 mg/80 mg), is a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor and inducer and may increase plasma concentrations of systemic lidocaine. For example, a 5-day oral aprepitant regimen increased the AUC of another CYP3A4 substrate, midazolam (single dose), by 2.3-fold on day 1 and by 3.3-fold on day 5.